Schedule a Consultation
Get help with depression today!
It's important to know that you are not alone.
Treatment-Refractory Depression
Treatment-refractory depression, also known as treatment-resistant depression (TRD), is a severe form of major depressive disorder (MDD) that does not respond adequately to standard treatments. Individuals with TRD may have tried several types of antidepressants, therapy, or combinations of treatments, but still experience persistent depressive symptoms that affect their daily lives.
Unlike typical depression, where symptoms may lessen with medication and psychotherapy, TRD continues to cause emotional, mental, and even physical distress despite these efforts. This can be incredibly frustrating for patients and may lead to a worsening of the depression if not addressed with specialized care.
Why Treatment-Refractory Depression Must Be Treated
Leaving TRD untreated can have serious consequences. Chronic depression can erode one’s quality of life, impacting personal relationships, job performance, and overall mental and physical health. Individuals with TRD are also at a higher risk of developing other health conditions such as anxiety, substance use disorders, and chronic illnesses. In severe cases, untreated TRD can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Because TRD can be so difficult to treat, specialized approaches are necessary. Options like advanced pharmacological interventions, ketamine therapy, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be considered. Tailoring a treatment plan to the individual, monitoring for changes in symptoms, and offering ongoing support are key elements to effectively managing treatment-refractory depression.
Don’t let TRD define your life. With the right care, even the most persistent cases of depression can be managed, giving individuals a path to a brighter, more hopeful future.
How TMS is Used to Treat Depression
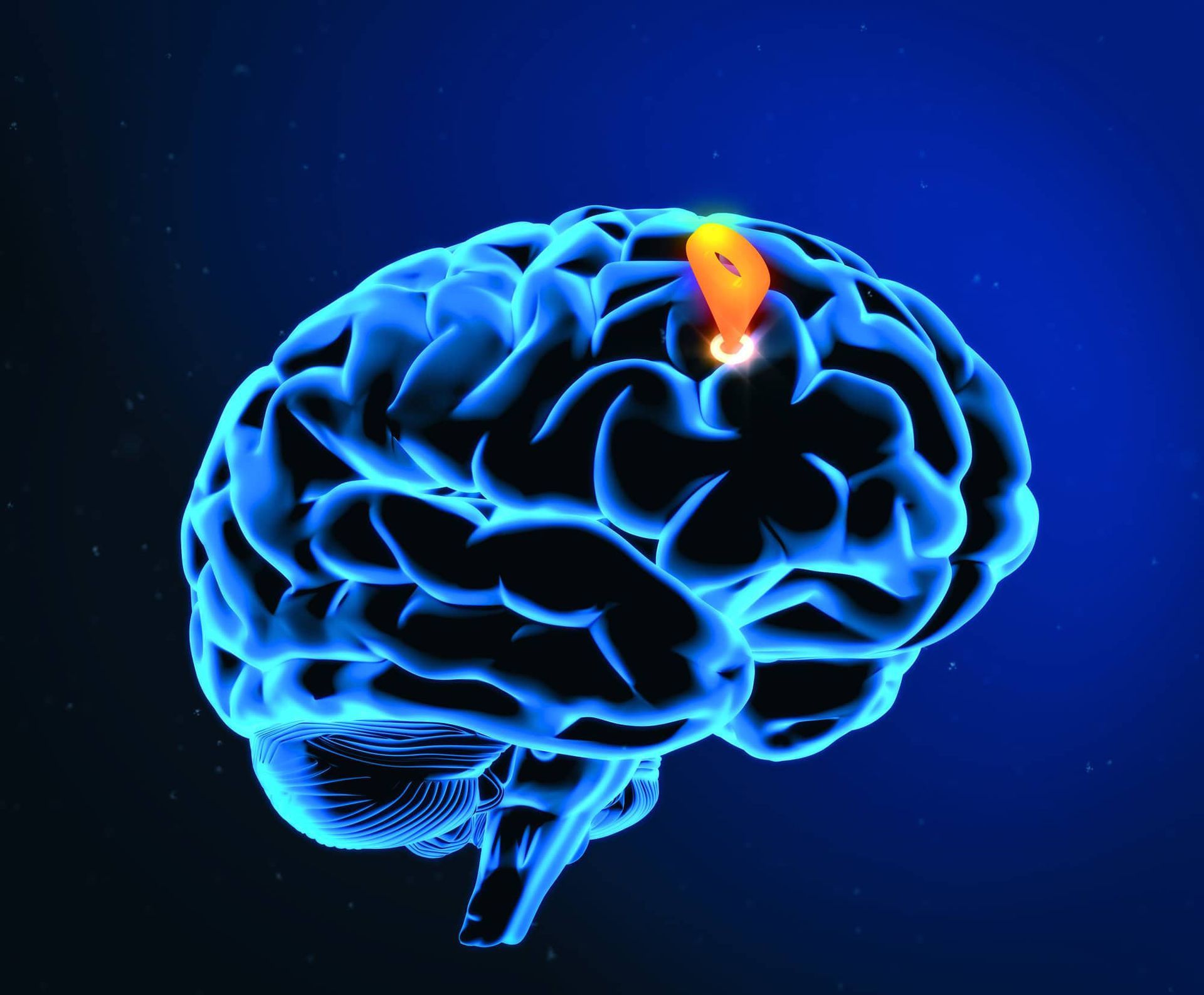
One promising treatment option for individuals suffering from treatment-refractory depression is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). TMS is a non-invasive, FDA-approved therapy that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain involved in mood regulation. For those who have not found relief with traditional medications or therapy, TMS offers a unique approach to managing depression.
How TMS Works
During a TMS session, a magnetic coil is placed on the scalp, delivering targeted magnetic pulses to the prefrontal cortex, an area of the brain often associated with depression. These magnetic pulses stimulate neurons, promoting neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself. By enhancing communication within the brain, TMS helps alleviate the symptoms of depression.
Benefits of TMS for Depression
- Non-invasive: TMS does not require surgery or anesthesia, making it a safe option for many patients.
- Minimal side effects:
Most individuals experience only mild discomfort during treatment, with few side effects compared to traditional antidepressants.
- No downtime:
Patients can resume their daily activities immediately after each session.
- Effective:
Research has shown that TMS can lead to significant improvements in depressive symptoms, particularly for those who have not responded to other treatments.
TMS therapy typically consists of daily sessions over several weeks, with each session lasting around 5-12 minutes. Many patients report a noticeable reduction in symptoms after completing their treatment course, providing hope and relief from the burdens of treatment-refractory depression.